With interest, I read an article Dzhipin Liu and Judith A. Curry (2010) - http://www.pnas.org/...336107.abstract (right - full text).
Abstract. The observed sea surface temperature in the Southern Ocean shows a substantial warming trend for the second half of the 20th century. Associated with the warming, there has been an enhanced atmospheric hydrological cycle in the Southern Ocean that results in an increase of the Antarctic sea ice for the past three decades through the reduced upward ocean heat transport and increased snowfall. The simulated sea surface temperature variability from two global coupled climate models for the second half of the 20th century is dominated by natural internal variability associated with the Antarctic Oscillation, suggesting that the models’ internal variability is too strong, leading to a response to anthropogenic forcing that is too weak. With increased loading of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere through the 21st century, the models show an accelerated warming in the Southern Ocean, and indicate that anthropogenic forcing exceeds natural internal variability. The increased heating from below (ocean) and above (atmosphere) and increased liquid precipitation associated with the enhanced hydrological cycle results in a projected decline of the Antarctic sea ice.
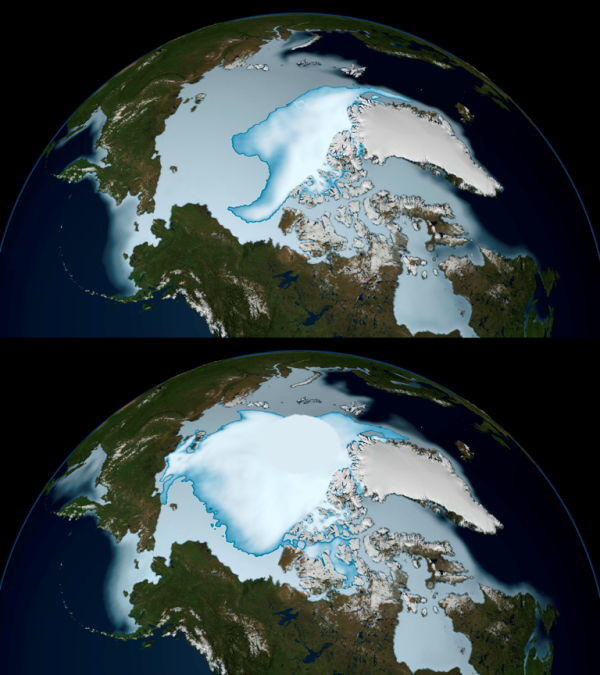
It turns leading climatologists associated modern growth of the Antarctic ice sheet with the "global warming" too. It refers to the warming caused by industrial greenhouse gases. Plus the effect of the ozone hole over Antarctica leads to the formation of clouds, and she - an increase in precipitation. Moreover (see abstract), "global warming" is additionally led to the fact that circulation of atmospheric moisture in the Southern Ocean accelerated. The result is that more snow falls. And it more flows to the Southern Ocean in the form of ice. Fresh and cold ice forms a layer of cold fresh water on the surface of the ocean. This layer creates obstacle to the warm masses of salt and heavy ocean water to reach the surface. Because of this, the area of the Antarctic ice now in winter has increased by almost to one million square kilometers, compared with its average size over the previous twenty years.
This explanation would have the right to exist, if the article contained at least some measure of this hypothetical movement of fresh water in comparison with those at the previous twenty years. But these measurements and such data does not exist, therefore speculative in general, the model of Liu and Curry just hangs in the air.
In support of the model of Liu and Curry an article by R. Bintanja were this year published - http://scholar.googl...AJ:OU6Ihb5iCvQC (pdf right).
Abstract. Changes in sea ice significantly modulate climate change because of its high reflective and strong insulating nature. In contrast to Arctic sea ice, sea ice surrounding Antarctica has expanded 1, with record extent 2 in 2010. This ice expansion has previously been attributed to dynamical atmospheric changes that induce atmospheric cooling 3. Here we showthat accelerated basal melting of Antarctic ice shelves is likely to have contributed significantly to sea-ice expansion. Specifically, we present observations indicating that melt water from Antarctica’s ice shelves accumulates in a cool and fresh surface layer that shields the surface ocean from the warmer deeper waters that are melting the ice shelves. Simulating these processes in a coupled climate model we find that cool and fresh surface water from ice-shelf melt indeed leads to expanding sea ice in austral autumn and winter. This powerful negative feedback counteracts Southern Hemispheric atmospheric warming. Although changes in atmospheric dynamics most likely govern regional sea-ice trends 4, our analyses indicate that the overall sea-ice trend is dominated by increased ice-shelf melt. We suggest that cool sea surface temperatures around Antarctica could offset projected snowfall increases in Antarctica, with implications for estimates of future sea-level rise
Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI).
This work confirms that such a mechanism does exist. However, this mechanism existed before, and its increasing influence in recent years in this work was not showed.
Another model was proposed in 2012 by Holland (British Antarctic Survey) - http://www.antarctic...l/publications/ (№ 20).
Abstract. The sea-ice cover around Antarctica has experienced a slight expansion in area over the past decades1,2. This small overall increase is the sum of much larger opposing trends in different sectors that have been proposed to result from changes in atmospheric temperature or wind stress 3–5, precipitation 6,7, ocean temperature 8, and atmosphere or ocean feedbacks 9,10. However, climate models have failed to reproduce the overall increase in sea ice11. Here we present a data set of satellite-tracked sea-ice motion for the period of 1992–2010 that reveals large and statistically significant trends in Antarctic ice drift, which, in most sectors, can be linked to local winds. We quantify dynamic and thermodynamic processes in the internal ice pack and show that wind-driven changes in ice advection are the dominant driver of ice-concentration trends around much of West Antarctica, whereas wind-driven thermodynamic changes dominate elsewhere. The ice-drift trends also imply large changes in the surface stress that drives the Antarctic ocean gyres, and in the fluxes of heat and salt responsible for the production of Antarctic bottom and intermediate waters.
Holland believes that the winds are the main cause of increasing the area of the Antarctic ice sheet. Winds in some cases, physically move the ice, in other cases, participate in the the thermodynamic changes of surface waters.
Despite the fact that among the authors of both models there was a discussion which about outlines can be read here - http://journalworld....rov-antarktiki/ , however, these two models suggest different phenomenons, in my opinion - complement each other, and explaining partial mechanisms of the Antarctic ice sheet origin, but do not say anything about why the ice in Antarctica became more.
At the same time, the orbital model of glaciation, which is based on the precession - http://dna-genealogy...man-migrations/, gives a simple explanation both to the increased melting of the Arctic and to the increased of ice formation of the Antarctic. These are two interconnected aspects of the same phenomenon.